Anna Brewer StudySmarter Originals. They are characterized by a carbon bound to three other atoms.
Ester Definition Structure Esterification Along With Properties Uses
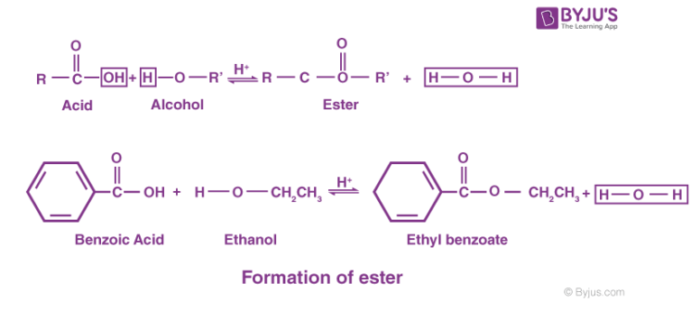
This is discussed in detail on another page but in general terms the two combine together losing a molecule of water in the process.

. Glycerides are fatty acid esters of glycerol. The oxygen atom is further connected to an aryl or an alkyl group. The formula for carboxylic acid esters is RCOOR where R and R are any organic combining groups.
It contains a carbonyl group the double bond. The general formula for an ester is R-COO-R where R and R are organic groups. During the twentieth century molecules were first constructed containing many ester linkages in single molecules.
HO Where R is an alkyl group. The structure of the ester contains a flexible functional group because the rotation about the COC bonds features a low barrier. Esters are derived from carboxylic acids and usually alcohol.
They are important in biology being one of the main classes of lipids and comprising the bulk of animal fats and. R 1 and R 2 are not necessarily the same as each. If it were hydrogen atom the compound would be a carboxylic acid Figure 154 The Structure of Esters shows models for two common esters.
They come in all shapes and sizes. The esters shown here are ethyl acetate a and methyl butyrate b. Esters feature a carbon-to-oxygen double bond that is also singly bonded to a second oxygen atom which is then joined to an alkyl or an aryl group.
General formula of esters. R 1 and R 2 are often carbon chains that can be either linear or branched and might also have other functional groups attached. Esters have the general formula RCOOR where R may be a hydrogen atom an alkyl group or an aryl group and R may be an alkyl group or an aryl group but not a hydrogen atom.
L and M is shown below. Here O represents oxygen and R. A general structure for esters J.
Esters are made from carboxylic acids and alcohols. Structure of Ester. Ethanoic acid ethanol ethyl ethanoate water.
Esters have the general formula RCOOR where R may be a hydrogen atom an alkyl group or an aryl group and R may be an alkyl group or an aryl group but not a hydrogen atom. Mass spectrometry ester miz of molecular ion peak 152 K 166 L 180 M 180 L M 3 Question. The singly bound oxygen is bound to another carbon.
An ester is an organic compound where the hydrogen in the compounds carboxyl group is replaced with a hydrocarbon group. Signifies that both R groups need not be the samedimethyl ether CH3OCH3Ethyl methyl ether CH3OC2H5. CH 3 COOH C 2 H 5 OH CH 3 COOC 2 H 5 H 2 O.
The general formula of the esters is CnH2n1COOCmH2m1 with values of n 0 1 2 3 and m 1 2 3. While carboxylic acid has the -COOH group the hydrogen is replaced by a hydrocarbon in an ester. Worked Example of How to Draw the Structure of a Simple Ester.
An ester is an organic compound that is a derivative of a carboxylic acid in which the hydrogen atom of the hydroxyl group has been replaced with an alkyl group. In some cases even an individual ester may have a similar smell to a natural aroma. HO Where R is an.
Describe the structure of the ester ethyl ethanoate. An ester is a chemical compound derived from an acid organic or inorganic in which at least one OH hydroxyl group is replaced by an O alkyl group as in the substitution reaction of a carboxylic acid and an alcohol. With sulphuric acid as a catalyst.
The ester functional group is. R can be a hydrogen but if R is hydrogen as it is in this example then the compound is a carboxylic acid. Oxygen is much more electronegative than carbon and so attracts the shared pairs of electrons in the double bond towards itself becoming partially negatively charged and.
As can be seen from the above the general formula for a simple ester is R-COOR where the prime on the second R merely means it that R may be different from the first R. Such molecules are called polyesters. OH w 3-Chlorobenzoic acid 3-Chloro-1-benzene carboxylic acid O 1-Chloro-2-benzoic acid 01.
The structure is the product of a carboxylic acid the R-portion and an alcohol the R-portion. When looking at the structure of an ester you can easily name it. Ester names are derived from the parent alcohol and the parent acid.
As can be seen from the above the general formula for a simple ester is R-COOR where the prime on the second R merely means it that R may be different from the first R. The general structure of an ester. Structurally an ester is an organic compound with an alkoxy OR group attached to the carbonyl group.
If it were hydrogen atom the compound would be a carboxylic acid Figure 154 The Structure of Esters shows models for two common esters. With sulphuric acid as a catalyst. A single bond to a carbon a double bond to an oxygen and a single bond to an oxygen.
R may be Hydrogen alkyl or aryl while R may be alkyl or aryl only. The general formula for an ether is R-O-R where R. The general formula for an ester is R-COO-R where R and R are organic groups.
The general formula for an ester is shown below. Esters feature a carbon-to-oxygen double bond that is also singly bonded to a second oxygen atom which is then joined to an alkyl or an aryl group. This group is polar.
Esters are a functional group commonly encountered in organic chemistry. Esters can be made from carboxylic acids and alcohols. Where the symbols R1 and R2 represent organic radicals.
An ester functional group has a carbon that is double bonded to an oxygen a carbonyl and single bonded to an O-R an alkoxy. L and M is shown below. Some examples include chocolate honey vanilla etc.
The colour coding refers to the name of the ester and not strictly to the structure. Esters are carboxylic acid derivatives in which the hydroxy group -OH is replaced by an alkoxy group -OR Esters contain a carbonyl centre which provides rise to 120 CCO and OCO angles. In fact an ester is the product of an esterification reaction between a carboxylic acid and an alcohol.
Remember that the CO part of the molecule came from the acid. Lets revisit the general structure of an ester. Esters are organic chemical compounds whose structure has the general form.
The chemical formula of an ester takes the form RCO 2 R. In the molecule below the. Use the mass spectrometry results to deduce possible structures for esters J L and M.
Question 4 The following is the general structure for a n R SR Ether O Ester Carboxylic acid Ketone The following is the general structure for a n O0 R R O Ether O Ester Carboxylic acid o Ketone D Question 6 Name the following II U C. The R group can either be a hydrogen atom or a carbon chain. A molecule of water is eliminated when a carboxylic acid combines with an alcohol to form an ester.
Esters feature a carbon-to-oxygen double bond that is also singly bonded to a second oxygen atom. The values of n and m indicate the numbers of. A general structure for esters J.
The esters shown here are ethyl acetate a and methyl butyrate b. When the ester is made the water that is lost comes from the whole.

Glutamine Chemical Structure Chemical Structure Amino Acids Lettering

Learn The Systematic Names And Structures Of Esters Found In Fruit

Functional Groups In Organic Chemistry With Diagrams Organic Chemistry Organic Chemistry Study Functional Group
0 Comments